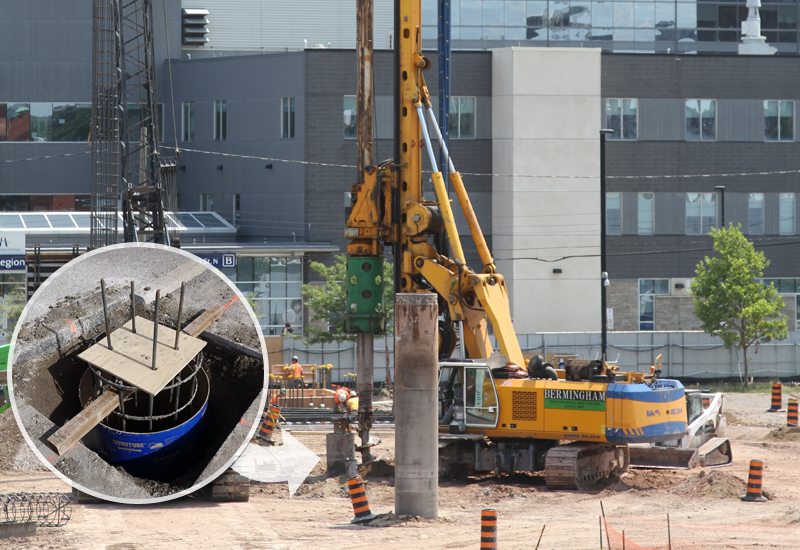
Bored Piles (Caissons)

Bored Piles, also known as drilled shafts, cast-in-place piles or caissons, are constructed by drilling and excavating a slender, cylindrical hole and backfilling it with reinforcing steel and concrete. Depending on the geotechnical conditions, a steel casing can be installed during drilling to hold back the sides of the excavation temporarily or permanently.
Advantages
- Caissons have a relatively large load bearing capacity. A single, large caisson can replace the need for several smaller piles and large pile caps.
- Caissons can be installed in most soil types and can be drilled into sound bedrock.
- Properties of excavated soils can be observed and compared to design data.
- Caisson construction generates less noise and vibration than other deep foundation
Applications
Caissons are ideal for foundations that require a large bearing capacity and a small footprint. They are often used for high-rise buildings, arenas, bridge piers and electrical transmission towers.

